CI/CD For Beginners
incomplete
Lesson 1: Introduction to DevOps
Waterfall Model
traditional approach to software development
development happens in a step-by-step process
Requirements Analysis
programmers accept teh client requirements and analyze it
Design
programmers then come up with a project plan and a design architecture
Development
programmers code the application as per project plan and design
Testing
ensure the application is error-free and meets the requirements
Maintenance
operations team monitors the application
❗❗❗ Disadvantages
any new requirements from the client will restart the development cycle
if the client is unhappy with the product, the entire project cycle is restarted
Agile Method
programmers create prototypes to understand client requirements
Feedback Loop
the entire process of building an application is broken down into small actionable blocks called sprints
✔✔✔ Advantages
client requirements are better understood because of the constant feedback
the product is delivered much faster as compared to a waterfall model
❗❗❗ Disadvantages
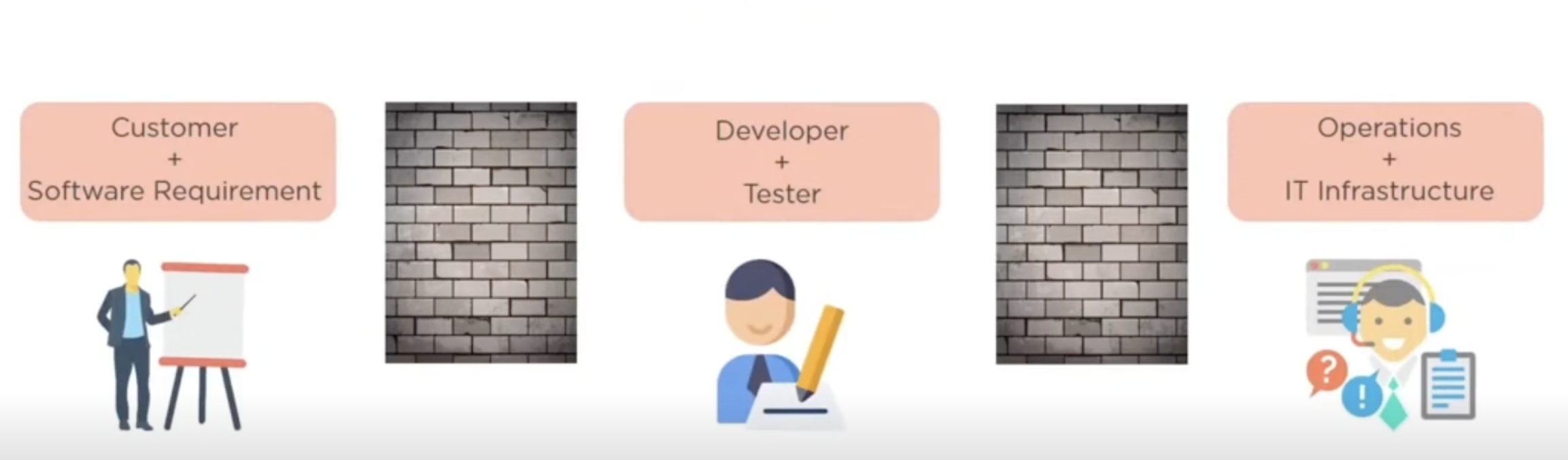
product gets tested only on developer computers and not on production systems
developers and operations team work in silos
developers submit the product to operations team for deployment
if the product fails in production servers, the operations team are clueless and send product back to development
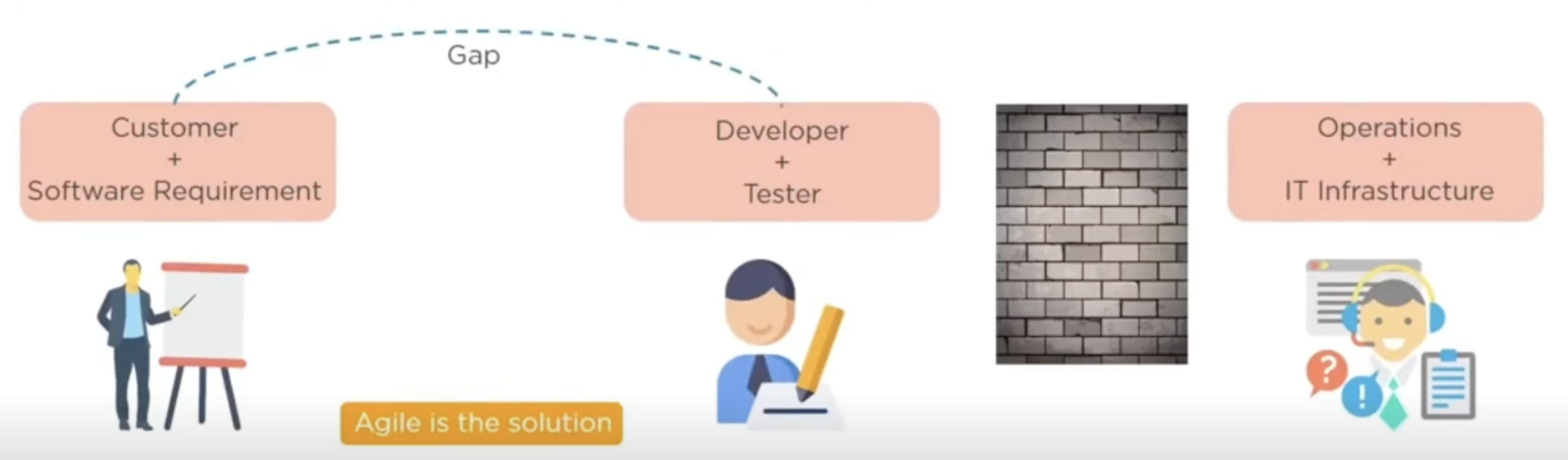
What is DevOps?
devops is an evolution from Agile model
addresses the gap between clients and developers
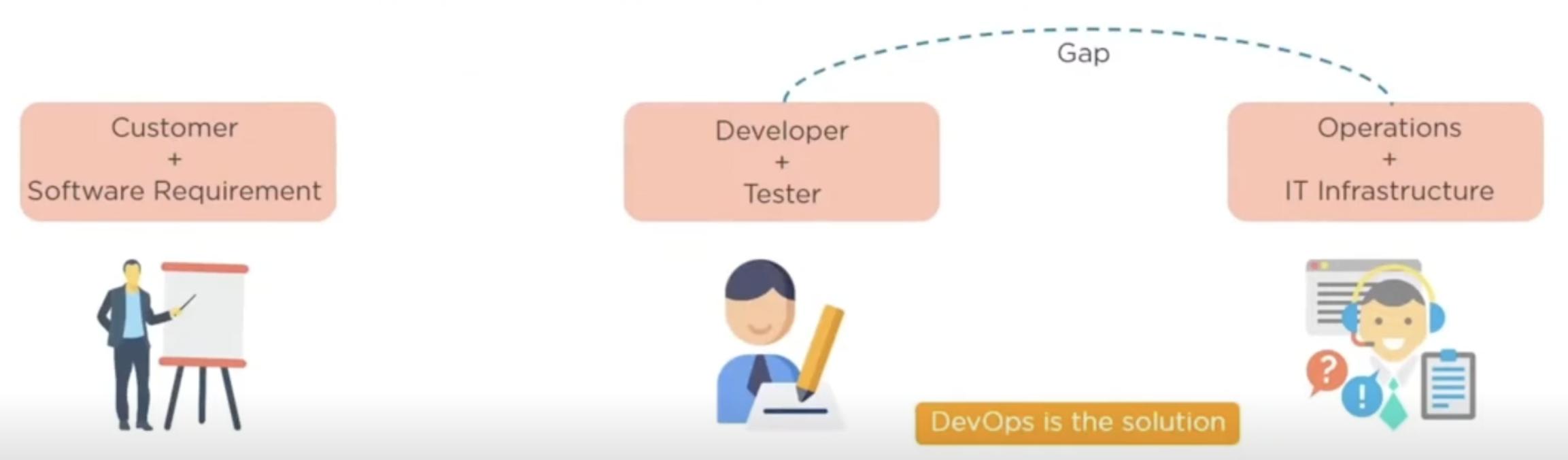
the development team will submit the application to the operations team for implementation
operations team will monitor the application and provide relevant feedback to developers
DevOps Phases
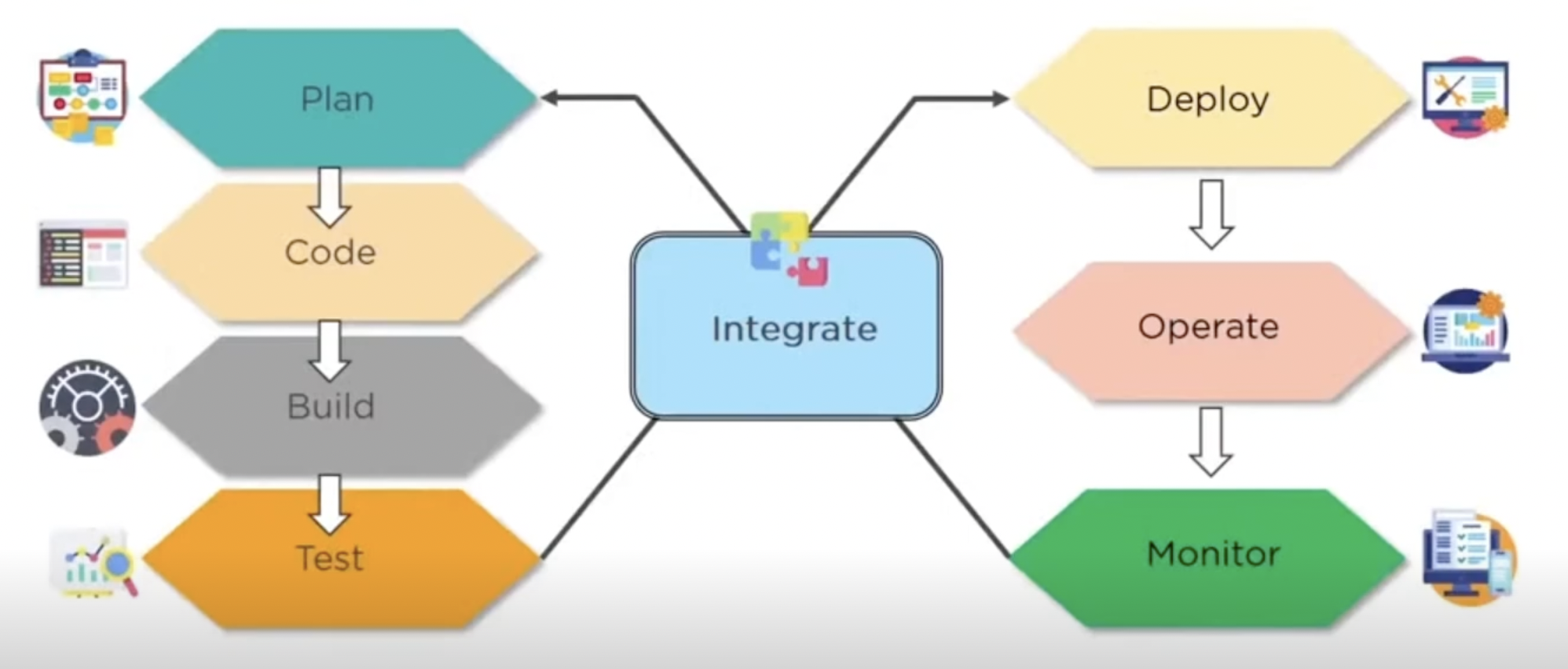
Plan: business owners and software development team discuss project goals and create a plan
Code: programmers then design and code the application and use tools like Git to store application code
Build: tools like Maven and Gradle take code from different repositories and combine them to build the complete application
Test: application is tested using automation testing tools like Selenium and JUnit to ensure software quality
Integrate: new features are integrated automatically to the already existing code base (Jenkins)
Deploy: application is packaged after release and deployed from development server to production server
Operate: once deployed, an operations team performs activities such as configuring servers adn provisioning them with the required resources (Chef and Ansible)
Monitoring: allow IT organization to identify specific issues of specific releases and understand the impact on end users
DevOps Advantages
time taken to create and deliver software is reduced
the complexity of maintaining the application is reduced
improved collaboration between development and operations teams
continuous integration and delivery ensure faster time to market
Lesson 2: What is Ci/CD Pipeline?
Overview of Continuous Integration
a development practice of code integration into a shared repository
each integration is verified by an automated build and automated tests
CI Process
Develop and compile
Preform unit tests
Integrate with databases
Perform pre-production deployment
Perform functional test and code labeling
Generate reports and analyze
developers must write unit tests that exercise each line of code
standard feature of CI is to have the process run all the unit tests in teh devs work branch before merging teh code into a common code base
if it fails a single test, then the code is NOT merged into the common code base
Overview of Continuous Deployment
an extension of CI
aims to reduce the time the development team takes between writing one new line of code and using it in production
for the most part CD is a highly automated process
scripts take over manual work during deployment
create the computing environment before deployment
automation reduces teh time it takes for code delivered from developer to end user and increase teh accuracy fo the code
Benefits
faster feedback from end users on each new feature as it is released to production
faster ROI for each feature as it gets development
Popular Tools in CI/CD
Jenkins
Travis CI
Bamboo
Team City
Gitlab
Continuous Integration with Jenkins
over 1000 plugins
integration with over 100 DevOps tools
orchestration of the DevOps tool chain
end-to-end CD pipeline management
Typical Phases
Code and commit - IDEs, Git, GitLab
Build and config - Maven, Gradle, Docker, Chef, Puppet, Ansible
Scan and test - JUnit, Cucumber, Sonar, Selenium
Release - uDeploy, CollabNet, Serena, MidVision, XLRelease
Deploy - Docker, .Net, Azure, AWS, OpenStack, JMWare
Continuous Deployment with Jenkins
Operational Stages
Code terminal
Storage
QA
Testing
Production
Continuous Integration with Team City
from JetBrains
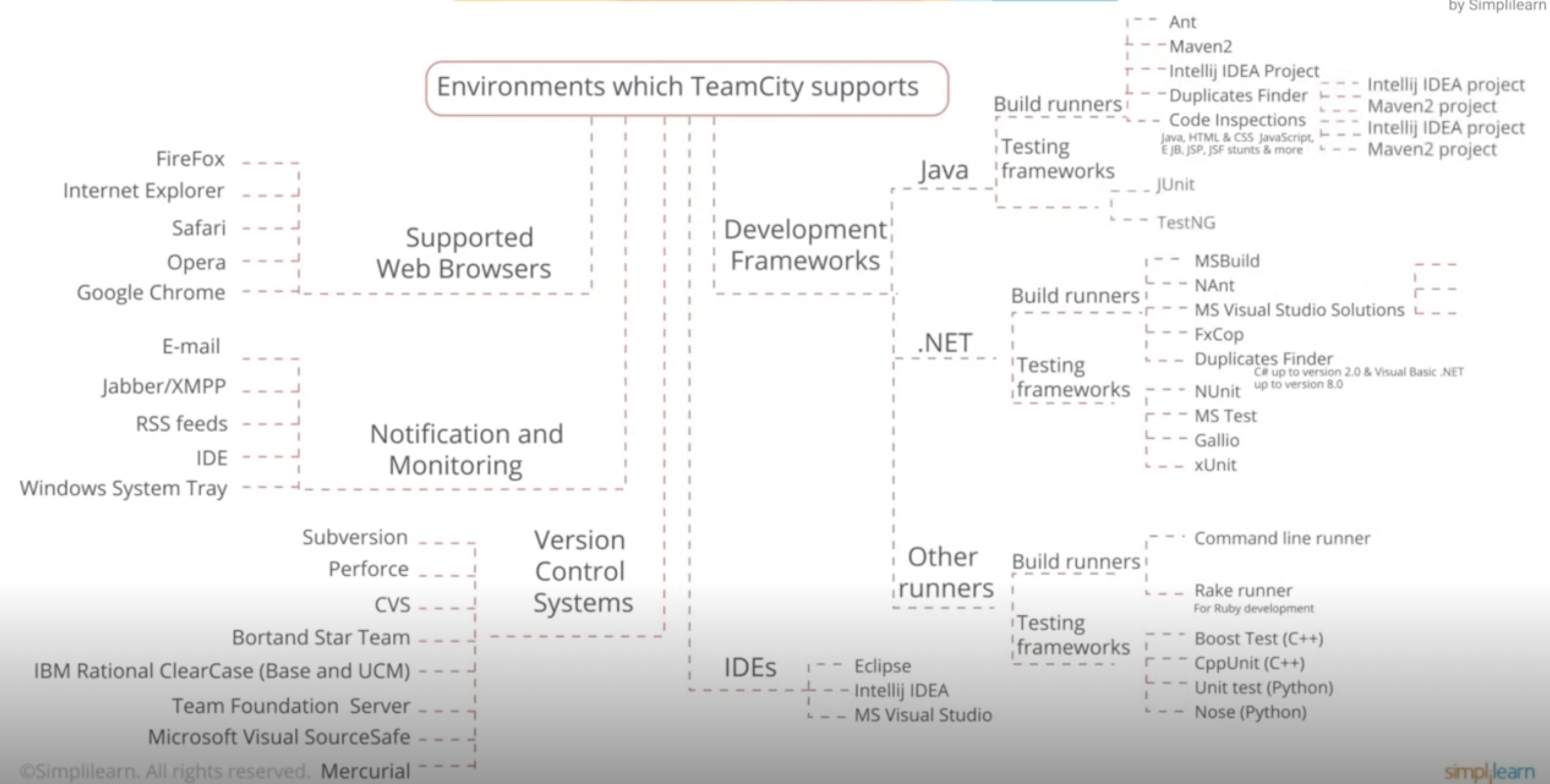
Continuous Deployment with Team City
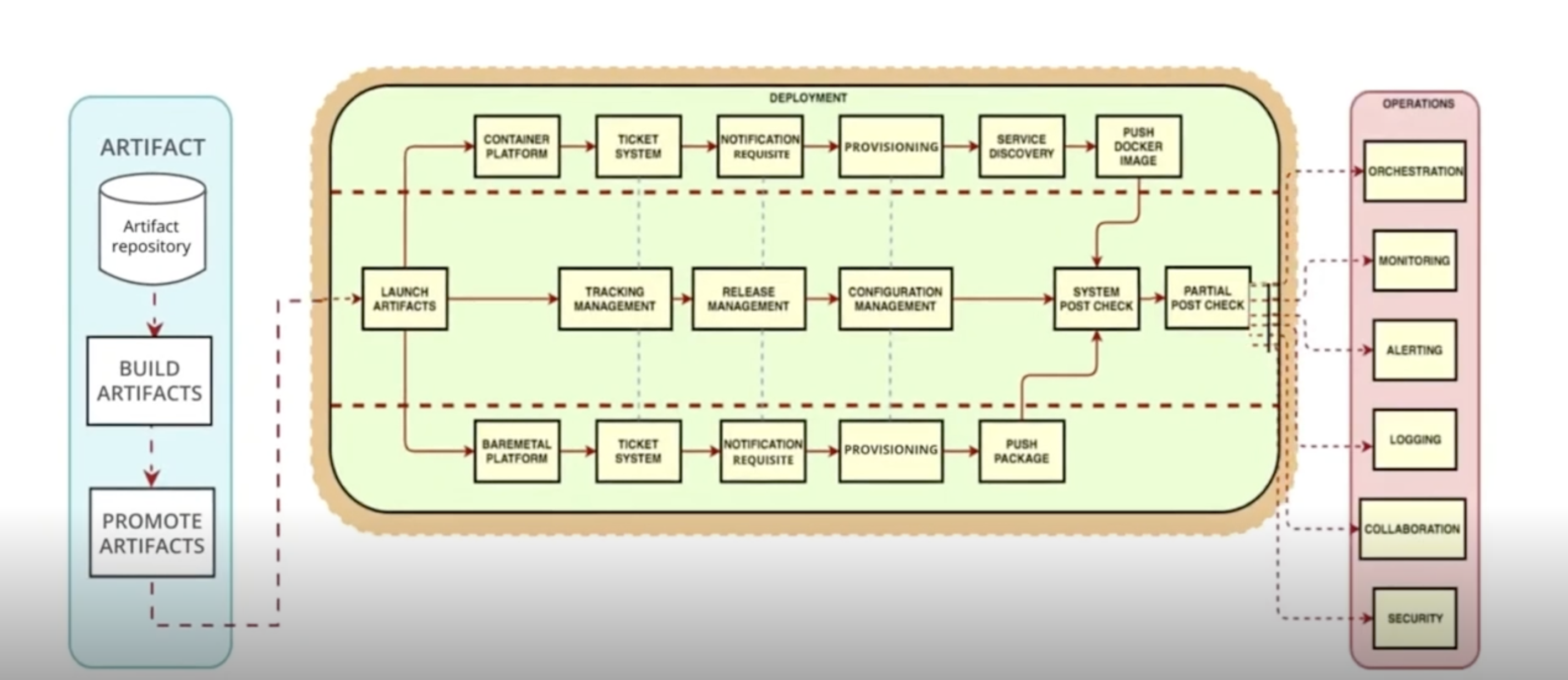
Lesson 3: What is Jenkins?
Jenkins as a Continuous Integration Tool
Java-based, open-source automation tool
functions as a server and is a software development and cross-platform tool used for CI/CD
CI Server
can be used as a CI server
can be used as a CD hub for a project
Distribution
easily distribute work across different machines and help trigger build, tests, and deployments to multiple machines and platforms faster
Cross-platform
IOS, .Net, Android development, Ruby and Java
Architecture of Jenkins
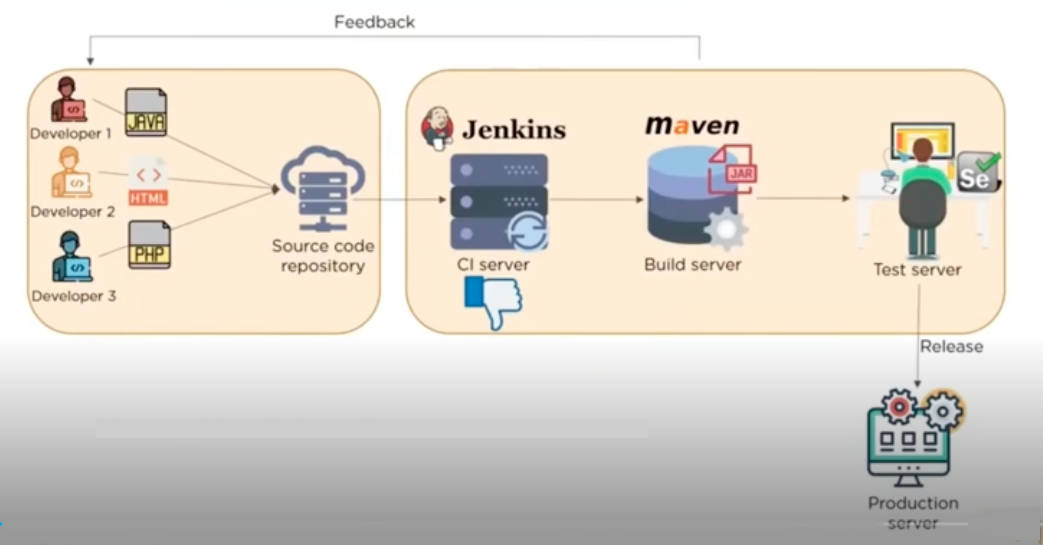
jenkins has classes like project and build
uses Jelly as the view technology
uses a file system to store its data
directories are created inside
$JENKINS_HOME
supports plugins which can plug into those extension points and extend the capabilities of Jenkins
Popular Features of Jenkins
platform independent
rich plugin ecosystem
support from large communities
scaling of large error-ridden integrations
automation integration enabling immediate detection and resolution of issues
open-source and user-friendly
easy to configure, modify adn extend
Build Status and Job Health
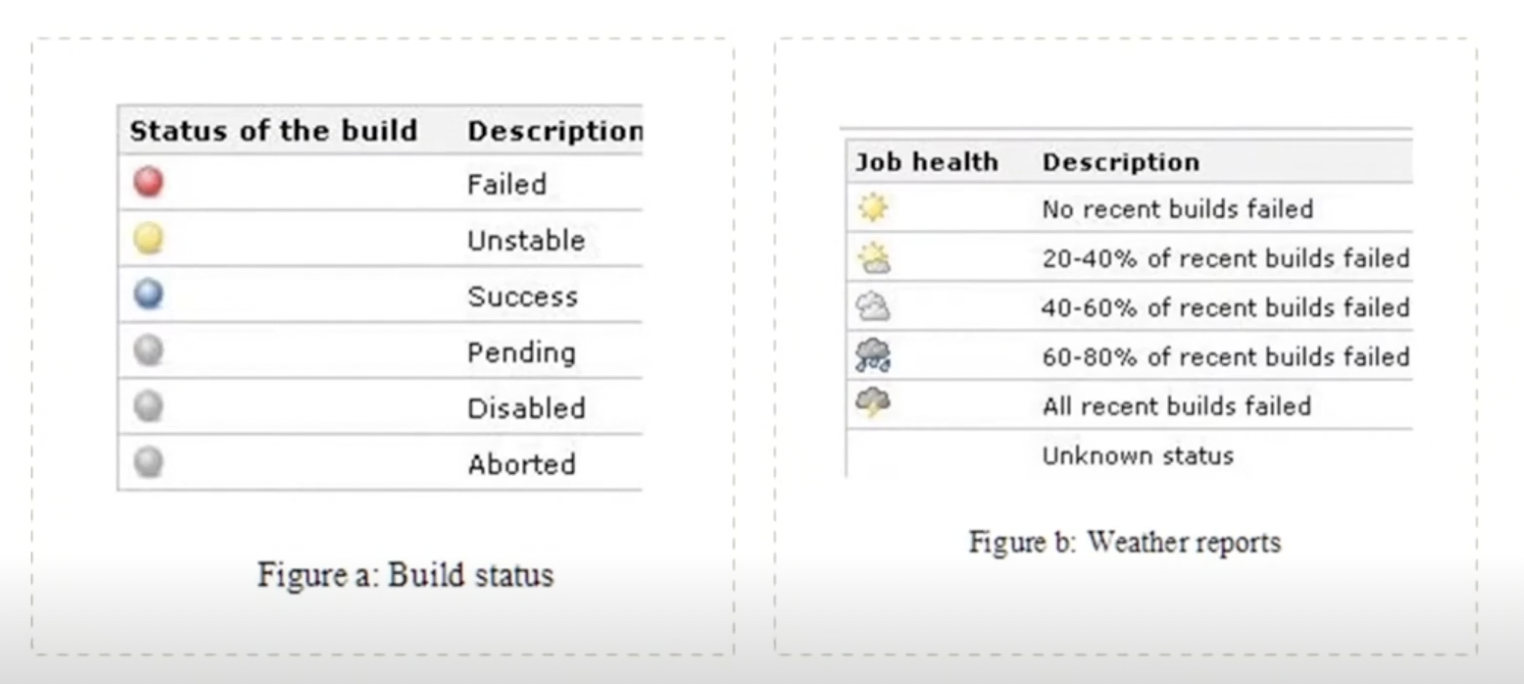
Summarize what the reader achieved by completing this tutorial.