Splunk: Zero to Power User
Introduction
What is Splunk?
Security Information and Event management (SIEM)
Network analysis tool that serves as a platform to conduct your big data analytics
Bring our data into Splunk, we read the raw events, and then we structure those events to make sense of the data that we're looking at
Take any kind of data structure your information is in, and is going to parse them and then create raw event logs for you to then search
Can create a bunch of different visual displays with the data you bring in and generate reports
Lets you tell the story of what's happening on your network and can give you insight to intelligence indicators you put into it and traffic that's traversing your network
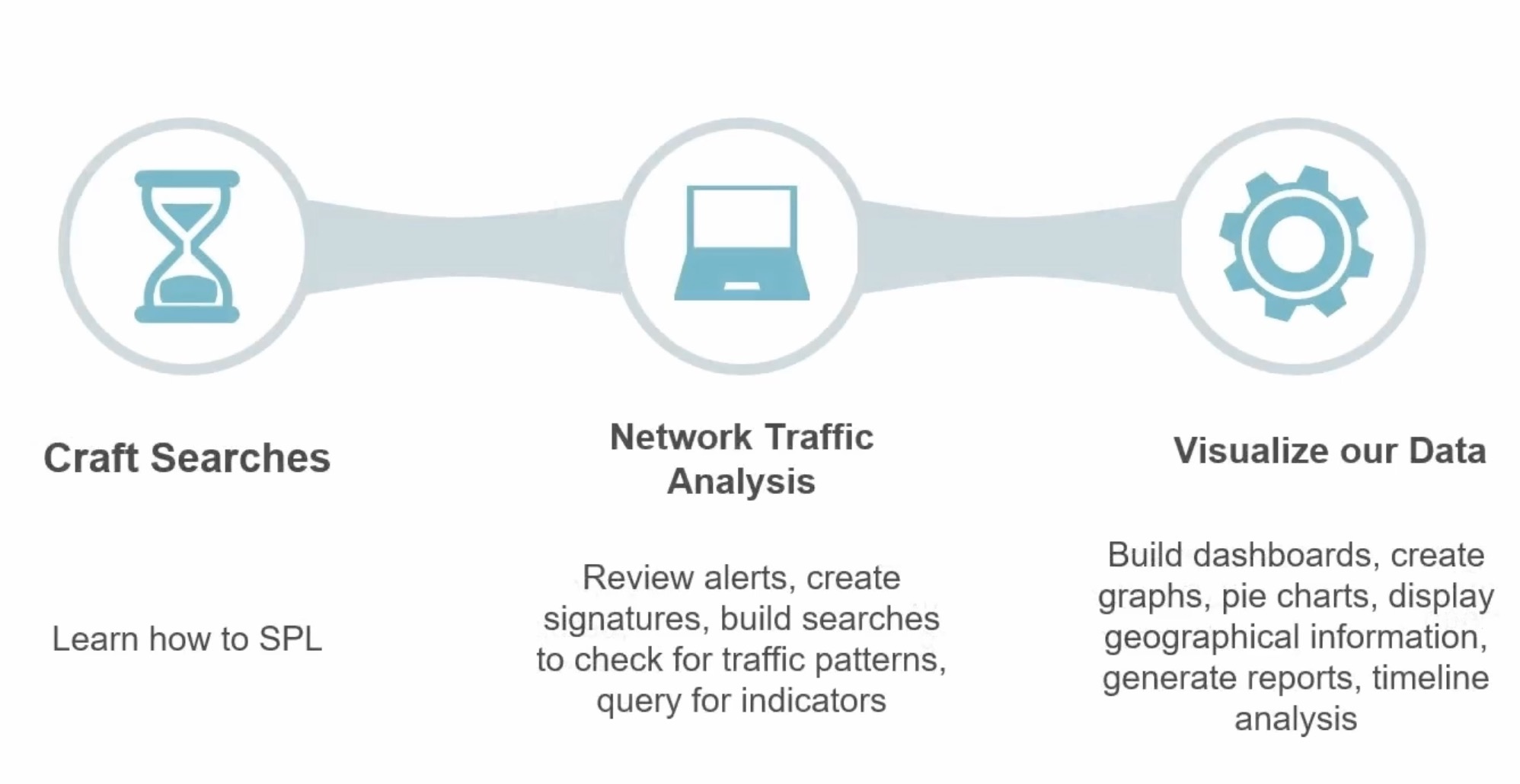
What Makes Up Splunk?
Big three components:
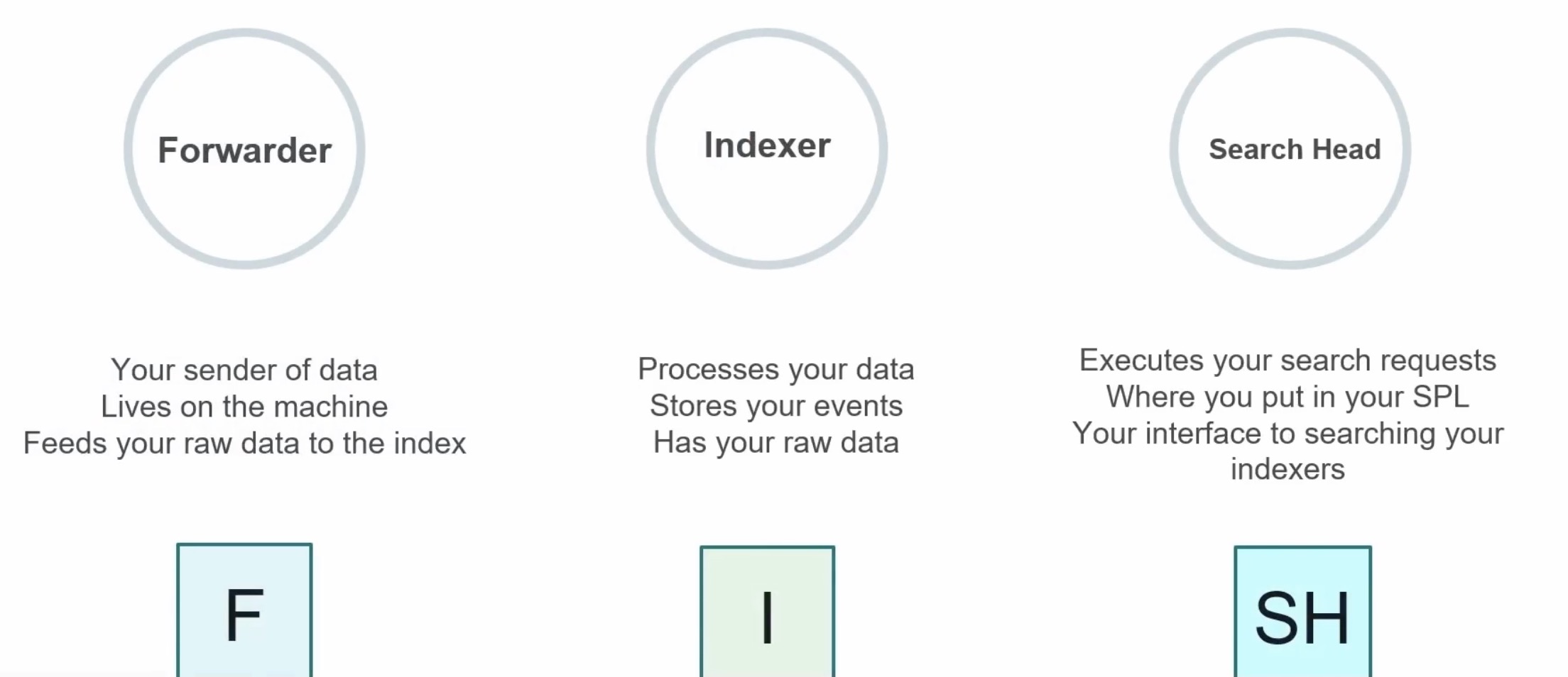
Forwarders
going to forward off your data
Indexers
going to index and process your data
Search Headers
going to allow you to query and search your environment
Forwarder
Three kinds:
Universal forwarder
Heavy forwarder
Intermediary forwarder
going to forward off the data of those raw logs to an indexer from the machine that it resides on
Indexer
going to take the raw data and process it
think of an indexer as a page
write one line at a time starting at the top going to the bottom until the page is full
processes those raw logs are going to get sent over in the form of buckets
for now, think of a bucket as a stored directory of data that lives on the indexer, and it's grouped by time of that data for the events because the events are processed into these time groupings
Search Head
leverage your search head searching by time
most efficient delimiter to set as it tells the indexer exactly where to pull the data from disk and where to search on the indexer's page
main interface for querying your data that resides in your environment
craft your spells here, execute your search requests, and then send those requests off to the indexers to be executed
Types of Splunk Deploys
Stand-alone
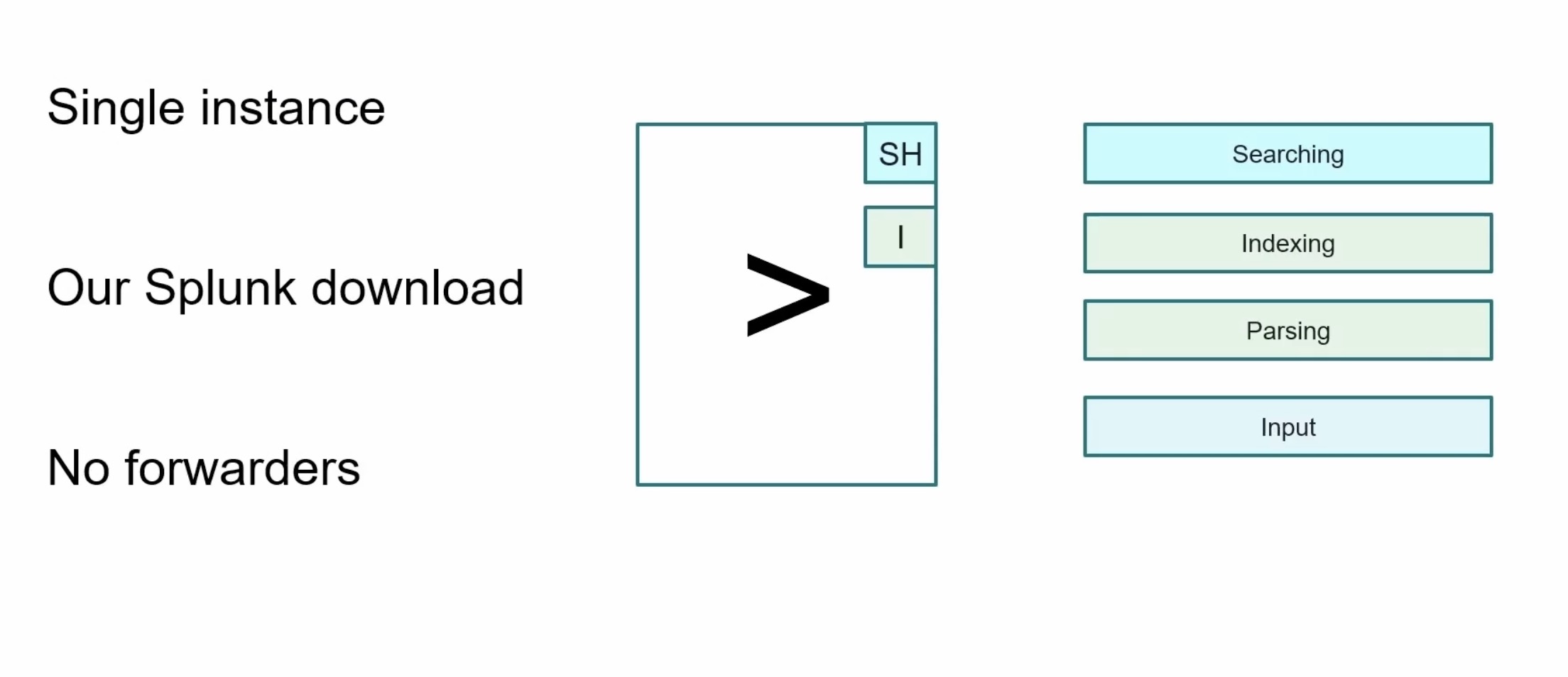
download Splunk on your local computer
Splunk server would function as the search head and the indexer
handle all those search requests and processing of the data
no need to deploy forwarders, so your inputs would reside with whatever configurations you make on that single server or your laptop
Basic
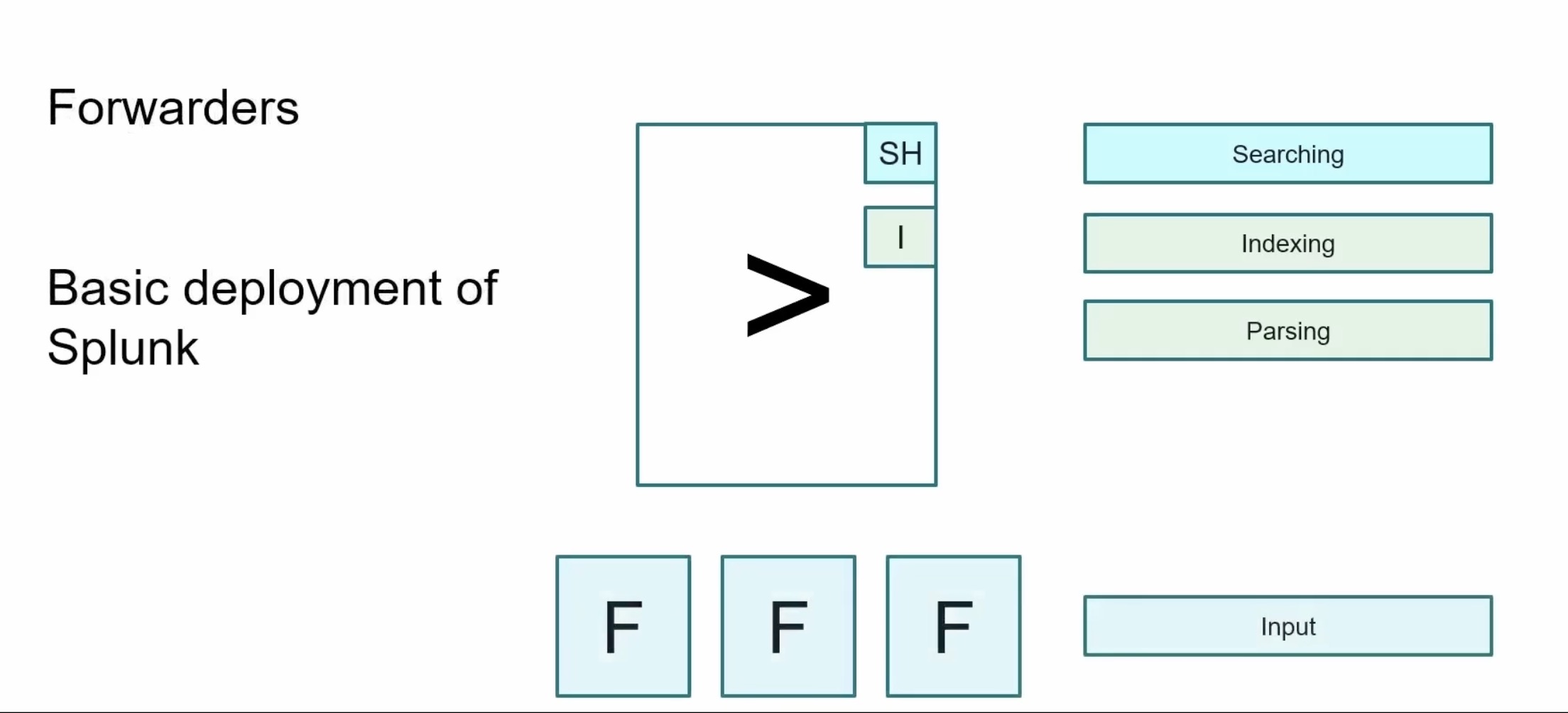
start utilizing forwarders that reside on a remote machines to forward the data from those machines back to the Splunk server
Splunk server is still going to be our search engine and our indexer, but the inputs can now be handled by setting up the forwarder agents out on our remote machines
Multi-instance
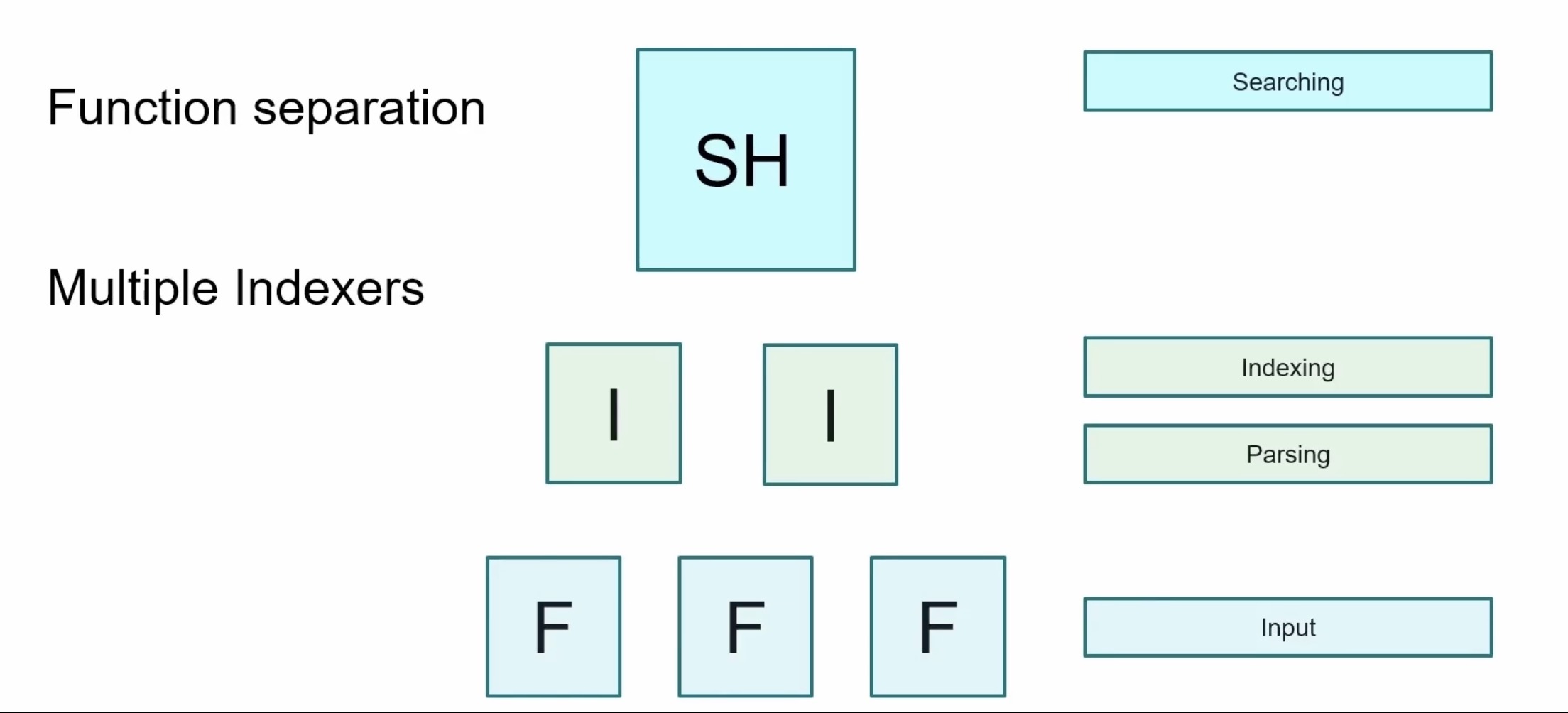
common for how most companies utilize Splunk for their large production environments
key here is functional separation from your search head
indexers and the forwarders each handle their own roles
search head search only
indexer index only
forwarders only forward
Clustering
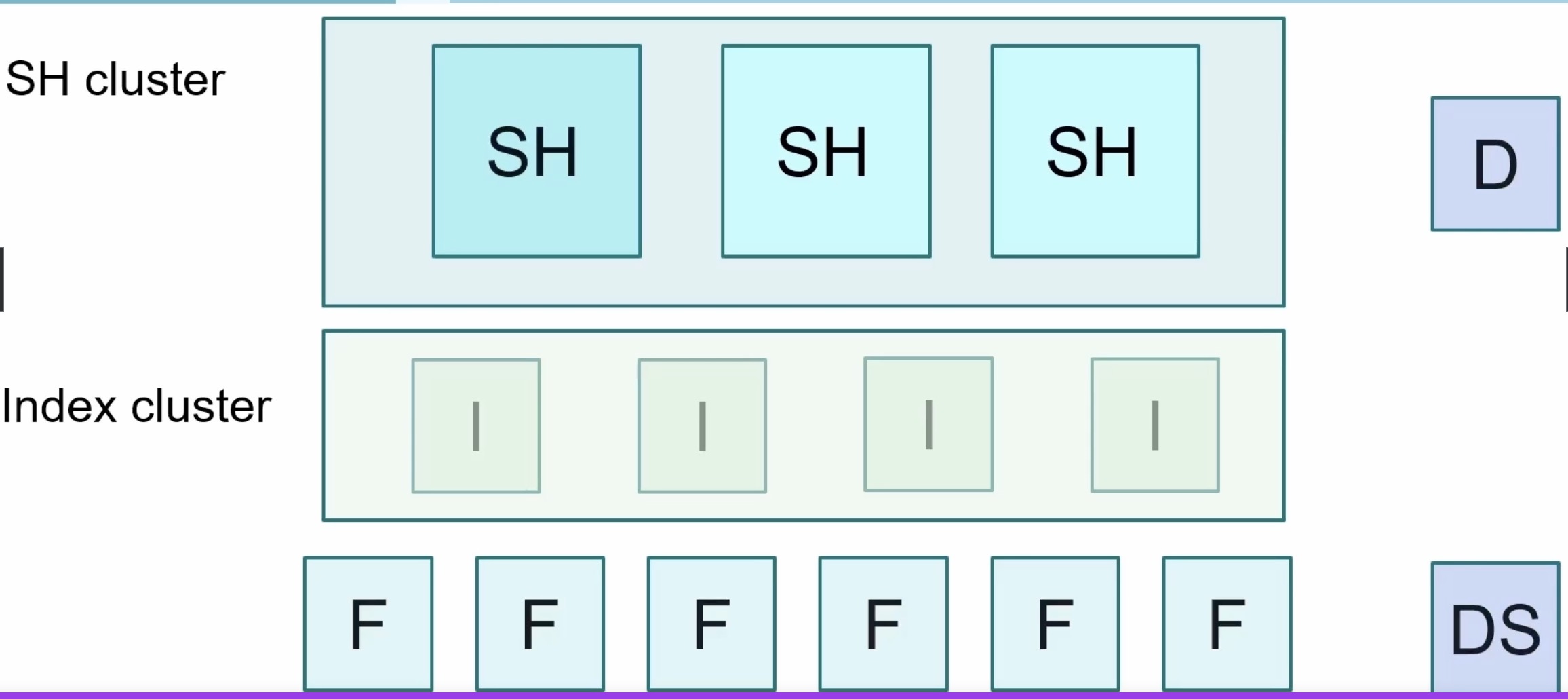
can increase your search capacity when we have a clustered search head
each user can collaborate their shared resources and knowledge objects
each search in a clustered environment should be a one for one replica of another search head in that environment, and you need a minimum of three search heads to have a clustered search head environment
a deployer is what you would use to manage your search, head, cluster environment
clustering your indexers can increase your data availability by doing data replication
replication factors that get involved with that
if you were to have hundreds of forwarders out in your environment, you would need to manage these through a deployment server
Getting Data into Splunk
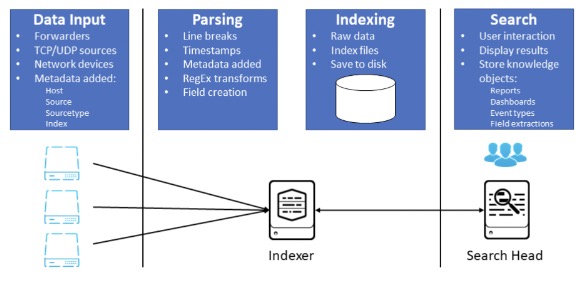
Forwarders
have the data, and they're forwarding it off, and your data is going to be in streams
If it's not coming from a forwarder, it may be coming from local logs, could be from a TCP port monitoring some kind of network traffic event, generations, etc.
anything in Splunk can really be inputted into the SIM
Parsing
handled by indexer
turned from streams into events and then also handled by the indexer
Indexing
compressed and written to disk
Search
query and display results
Input Types
Http event collector
log files
network traffic
etc.
Metadata
host-who sent the data
source-path to the data
source type-how the data will be formatted
index
App vs Add-on
App
something that can be launched and has a GUI component
usually reside on the search head and visibly displayed in the drop-down in the app's menu
Add-on or technology add-on (TA)
can also reside in the drop-down in the app's menu, but need to change the visibility settings for add-ons to be displayed there
added to Splunk instance for additional functionality
usually runs in the background and also usually vendor specific for the type of data involved
workstation display does not change
can land on indexers, search head, or forwarder
The Basics of Searching
Search Types
Keywords and phrases
designate phrases inside
""
File paths
Wildcards
LIKEfunction with the percent( % )symbol as a wildcard for matching multiple charactersunderscore
( _ )character to match a single characterasterisk
( * )character as a wildcard to match an unlimited number of characters in a string
Boolean Operators
ANDORNOT(exclude results from your search)
Comparison Operators
Operator | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| field=foo | Multivalued field values that exactly match "foo" |
| field!=foo | Multivalued field values that don't exactly match "foo" |
| field<x | Numerical field values that are less than x |
| field>x | Numerical field values that are greater than x |
| field<=x | Numerical field values that are less than and equal to x |
| field>=x | Numerical field values that are greater than and equal to x |
!=(value does not match the value you specify)
Knowledge Objects
tools and useful things to take advantage when conducting analysis
What are Knowledge Objects?
a set of user-defined searches, fields, and reports that enrich your data and give it structure
Tools
conduct analysis, enrich your events
Fields, field extractions, a lookup, tags, a field alias, data model or a saved search
Teamwork
shareable, reusable, and searchable based on permission sets
How are they managed?
Knowledge Manager
Ruler of the KOs
a person who provides centralized oversight and maintenance of KOs for a Splunk environment
Ex. Owner of a dashboard
Naming conventions
<Group name>_<type>_<description>Ex. SOC_alert_LoginFailures
Permissions
Private
only the person who created the object can use or edit it
This app only
objects persist in the context of a specific app
All apps
objects persist globally across all apps
Show Me the Fields
What are fields?
key-value pairs
searchable by name
ability to search mutliple fields at once or exclude fields from a search
created by Splunk or recognized from an Add-On
Meta-fields
Source
Source-type
Host
Making Use of Your Fields
you can create more seleccted fields
!= vs NOT
index=web sourcetype=access_combined categoryId!=SPORTS
This will tell Splunk to search for everything that does not contain the field value of sports for that field
index=web sourcetype=access_combined NOT categoryId!=SPORTS
will tell Splunk to search for everything that does not contain the field value of sports and all events where the category ID field doesn't exist
Search Processing Language (SPL)
Splunk syntax and colors
Orange - command modifiers
tell the search what you are looking for
can include your boolean operators, your keywords, or your phrases with
asorbyclauses setOR,NOT,AND,as,by
Blue - commands
tell Splunk what you want to do with the results
Stats,Table,Rename,Dedup,Sort,Timechart
Green - arguments
these are the variables that you apply to the search, usually to a function
Limit,Span
Purple - functions
tell your search to do things such as perform mathematical functions or calculate fields
Tostring,Sum,Values,Min,Max,Avg
Building effective SPLs
index=web OR index=security | stats sum(bytes) as Total_Bytes | eval Total_Bytes = tostring(Total_Bytes, "commas")
index=web OR index=security
pull all data from disk
name you indexes and meta-fields
stats sum(bytes) as Total_Bytes
set your command
what are we trying to do
eval Total_Bytes = tostring(Total_Bytes, "commas")
determine your functions
do we need to calculate results?
call your arguments
what fields are needed?
The search was built from left to right, starting with determining where the data resides, setting the calculations, and then formatting the results, how to be displayed
Table, rename, fields, dedup, sort
tablemake a table of the results based off the variables and arguments you set in your search.
renamerename the fields that currently exist in the data or rename fields that you've calculated and built in your searches
fieldsallows you to call on fields you want to include or exclude in your results
dedupstands for a duplicate and it will remove duplicated values from the results from the fields you select to duplicate
sortwill sort your results based off the arguments you set
Transforming Your Search
What is a Transforming Command?
search command that orders the results into a data table
transform the specified cell value for each event into numerical values that Splunk can use for statistical purposes
searches that use transforming commands are called transforming searches
Three Transforming Commands
Top
finds the top common values of a field in a table
top 10 results by default
can use with arguments
Rare
finds the least common values of a field
opposite of top
Stats
calculate statistics
count, dc, sum avg list, values, etc.
What are the Events Telling Me?
Transaction Command
Events can be grouped into transactions based on the associated and related identified fields
helps enumerate that relation
Arguments
maxspan
Max time between all related events
Ex:
maxspan=15m
maxpause
Max time between each event
Ex:
maxpause=1m
startswith & endswith
Set your variables for keywords, Windows EventIDs, or other searches of interest
Ex:
startswith=4624&endswith=4647
Investigating your events
Events that span time
they can come from multiple hosts, relate to one host of interest
Grouping of events
show the entire conversation, from start to finish in one view
Aid investigations
relate user activity for logins, session lengths, browsing history, etc.
Log validation
check to see if data is related to network logs of interest, website traffic, emails, etc.
Transaction vs stat
Transaction | Stats |
|---|---|
slow and will tax your environment | faster, more efficient searching |
granular analysis (logs, user behavior, conversations | looking at larger pools of events for trend analysis (no limit on number of events returned) |
small scope on one item of interest | broad searching and grouping events |
correlations need to be found from start to end | mathematical functions needed |
Manipulating Your Data
Eval command
Calculates fields
does the math you ask:
+, -, *, /, AND, XOR, >=, ==
Functions friendly
just like stats, it takes plenty of functional arguments
ifnullcidrmatchlikelookuptostringmd5nowstrftime
if the field already exists, it will overwrite that field, but it won't modify the underlying data already written to the disk
Create new fields
Eval will take the results of the SPL into a field that is existing, or create a new one
Converting data
tell Splunk to display a field vale of bytes to megabytes by providing the math in a eval statement
Strftime,strptime
where and search commands
Where | Search |
|---|---|
can't place before the first pipe in the SPL | place it anywhere in the SPL |
comparing values, or searching for a matching value | search on a keyword, or matching value |
use with functions | search with wildcards |
think boolean operators=where | think expressional searches=search |
Fields, Part 2
Field extraction methods
Regex - unstructured data
Delimiters -structured data
Commands -work with rex & erex in SPL
erex & rex commands
rex
regex pro
using regex to create a new field out of an existing field
have to tell what field to extract the data from
erex
aids in generating the regex for the extraction
must provide examples
Lookups
What is a lookup?
A file
mostly static data that is not in an index
Ex: csv of all employees
A tool
add additional fields to search for
fields will be added to the fields bar menu
How to use one
Data enrichment
add information and store it in a table/file format to then search
Commands
Lookupused to load the results contained in the lookup
can be used to just view the data
can be used as a form of validation
inputlookupused to search the contents of a lookup table
outputlookupused to write to that lookup table
OUTPUTthis argument when added will overwrite existing fields
OUTPUTNEWthis argument when added will not overwrite existing fields
Create or Upload
select a file to upload or make one to reference
Making a lookup
Navigate to
Settings>Lookup table filesClick
New Lookup Table File
Visualize Your Data
Types of visualizations
Tables
Charts
Maps
Visualization commands
timechart
time series will display statistical trends over time
single or multi-series
to get multi-series, you need to have
chartortimechartcommand in the search
ex:
Span=1d
chart
line, area, bar, bubble, pie, scatter, etc.
stacking available
remove empty values
Useother=fUsenull=f
stats
can easily alter any stats table
Options for panels
stacking
On= events are vertically stacked (top to bottom)Off= counts are horizontally stacked (left to right)
overlay
ex: add two line charts over each other
Trellis
display multiple charts at once
Multi-series
On=y-axisto split for each valueOff=allfields share the y-axis
Visualizations, Part 2
Additional commands
iplocationadd location information to visualizations
can be towns, cities, countries or just lat and long
geostatscalculate functions to display a cluster map
must be used with lat and long fields
all other arguments are optional
latitude,longitude,globallimit,locallimit
addtotalsadd multiple values together on a chart, compute total sums of values
Fieldname,label,labelfield
trendlineoverlay on a chart to show the moving average
sma(simple moving average),ema(exponential moving average),wma(weighted moving average)needs the functional trend type you're using for that field that you're calculating that function from included in the command
need you to define an integer value for the period that you want to set
Reports & Drill Downs
Reports
What are reports?
a saved search
anything that is a search can be saved as a report
live results
re-run a report or set it to run on a schedule
Shareable knowledge object
let anyone view your reports, or add them to a dashboard for people to reference
ex:
Audit_Report_LicenseUseage
Drill-down functionality
Actions
link to search
link to dashboard
link to report
$tokens$
tokens play a key role in passing variables from panel to panel
values that we can pass within a dashboard or search to optimize the shared values of what we want to search
used to allow for user input to be taken and then searched against
Export
export as a PDF, print, or include a report
Make a home dashboard
Navigate toSettings > Dashboards > Edit > Set as Home Dashboard
change in your preferences what you launch into after login
Alerts
What are alerts?
saved searches
run on a schedule
run real-time
content matches
fire when a condition is matched
create trigger actions
log
send email
webhook
custom action
create trigger conditions
per result
no. of results
no. of sources
custom
throttle
Welcome, Tags, & Events
What is a tag?
quick reminder
what was it that I was trying to see again
aid for reading data
create as many tags as you want
case sensitive
typing matters when searching
What are event types
highlighter
make them colors, mark events with similar criteria
like a report, but not
save searches as specific event types, sort into categories, no time range
ex:
status=400can be saved as "Not Found"
more specific
set strings, field values, & tags
Macros
What are macros?
shortcuts
fast, saved off searches to run by name
Repeatable
macros never change unless you edit them
expandable
CTRL+SHIFT+Eon windowsCMND+SHIFT+Eon macs
macronamerun with the use of backticks, not single quotes
macros can take one or more arguments
if you want use arguments, you must surround them with parenthesis
Making a macro
Navigate to
Settings>Advanced search>Search macrosClick
Add newto create one
Workflows to Save You Time
Introduction to workflow actions
Assess actions
depending on use case, there are three available workflow actions which provide different functionalities
Create workflow action
using Splunk web, create a new workflow action to either push, pull or search data
Configure workflow action
within the web GUI,configure the previously determined action type with a 3rd party source
Validation
check to see if data is being pushed, pulled searched for after configuration
Splunk provides two main workflow actions:
GET
create HTML links to interact with sites
ex:Google searches, query WHOIS databases
POST
generate HTTP POST request to specific URI
ex: create entries in management systems, forums
Another workflow action is Search
Launch secondary searches using field values
ex: occurrences of IP addresses over events
GET Workflow action
Navigate to
Settings>Fields>Workflow ActionsClick
Newto open up a workflow action form
Data Normalization and Troubleshooting
Field aliases
ex:
srcip_addresssourcenormalize your data
apply multiple fields to the same field alias
make searching and training easier amongst users
thing CIM
Navigate to
Settings>Fields>Field Aliasesclick
New Field Aliasto create one
Calculated fields
like a macro but for fields
save off quick math to output fields using the
evalcommand, then use it in a searchNavigate to
Settings>Fields>Calculated Aliasesclick
New Calculated Fieldto create one
Buckets
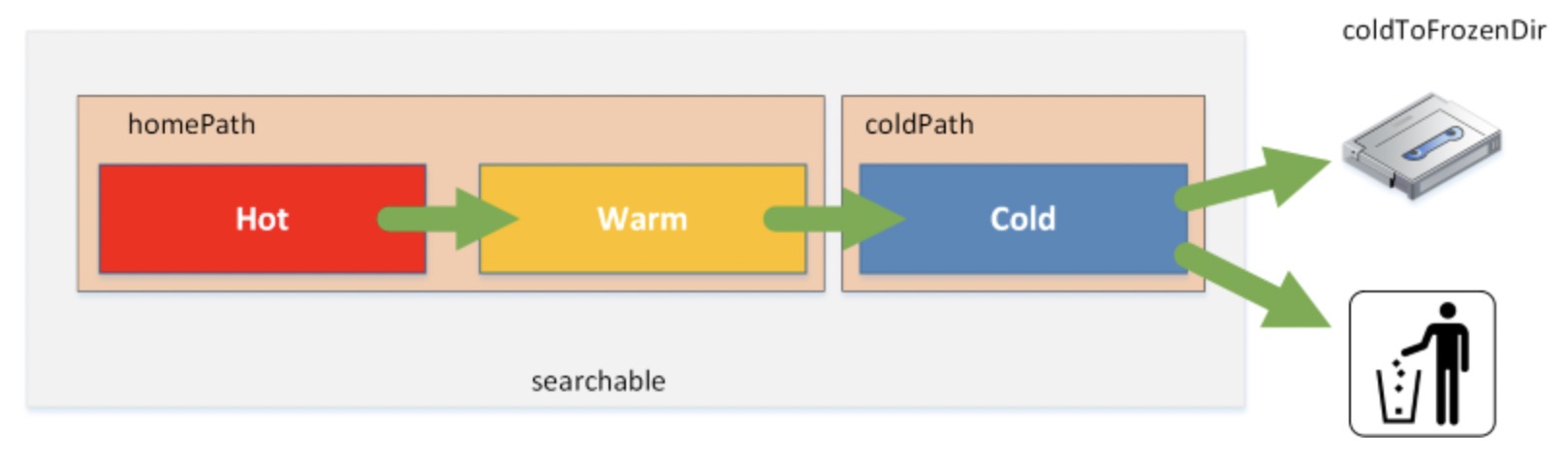
Hot
data is being actively written to the bucket by the indexer
*only writable bucket
data is searchable
Warm
data is getting older
rolled from hot > warm
data is searchable
Cold
data is even older
data is searchable
Based on the retention policy with Splunk, the data will eventually roll over to the frozen bucket and the data will either get archived or deleted
Frozen buckets are not searchable
Job inspector
tool | information | tips |
|---|---|---|
Allows you to trouble shoot your search efficiently, or reason for failing | Gives you information about how the search completed, and time it took to run | If you are using a KO wrong, it will suggest how to correct your search |
Datamodels
What are datamodels?
Hierarchical
parent and child relationship
root dataset
Dataset search
select the specific datamodel and dataset you want to search
Normalization tool
CIM compliant
data mapping to a model that fits that type of data
Large data searches
search larger amounts of data faster, with tstats and accelerated datamodels
Commands
datamodel
tstats
pivot
Syntax
| datamodel <Data_Model> <Data_Model_Dataset> search | search sourcetype=<your:sourcetype> | table * | fields - <List any statistics columns you do not want to display> | fieldsummary
| tstats <stats-function> from datamodel=<datamodel-name> where <where-conditions> by <field-list>
Examples:
| datamodel | Network_Traffic All_Traffic search | search sourcetype=cisco:* | stats count by sourcetype
| tstats count from datamodel=web
| tstats \summariesonly` count from datamodel=Intrusion_Detection.IDS_Attacks where IDS_Attacks.severity=high OR IDS_Attacks.severity=critical by IDS.Attacks.src, IDS_Attacks.dest, IDS_Attacks.signature, IDS_Attacks.severity`
The Common Information Model (CIM)
What is the CIM?
A Model
a model to use and reference a common standard of operations for how all data is handled
An Application
provides 22 pre-configured data models for you use and build off, tune and map your data to
CIM Add-On and CIM Add-On Builder are available for free
Data Normalizer
in the end, all fields can have the same name
all apps can coexist together
How to leverage its features
Normalize data
Assistance
leverage it when creating field extractions, aliases, tags, etc.
Datamodel command
be able to run common searches that span larger amounts of data
Why is it important
Splunk Premium Apps
Splunk ES relies heavily on CIM compliant data
Health Check Tool
perform faster, more efficient searches that leverage searching data models instead of raw events
Ease of Use
find commonality among Splunkers
Audit
check to see if all our data going into Splunk is CIM compliant