Clean Code
incomplete
Section 1—Getting Started
What is clean code?
Is this clean code?
Looks like a function that creates a user with an age and return that user object into a variable.
Here is the full code:
dirty-code-1.py
So, as it turns out, this does not create a user at all.
It's a function that creates other functions, so it's a factory function or a higher-order function, and these other functions which are being created, turn out to be validation functions.
We pre-configured them with a certain value, for example, 31. And then we get a function, which we can call thereafter to compare another value against that created value.
And we either check for that value being smaller or bigger, depending on whether we chose max or min as a parameter for creating our validation function.
Because there's one thing which clean code certainly is not. It's not code that just works.
The example I showed you will work but it's still not clean code because clean code is not about whether code works or not. Instead, it's about whether code is easy to read and understand.
It turns out that as a developer, we spend quite a lot of time reading code, understanding code, for example, because we have to go back to code we wrote in the past to fix a bug or add a feature,or because maybe we need to dive into some code written by a colleague or by some other developer.
So we need to read a lot of code and therefore, reading code and understanding code should be easy because if it's hard, we lose a lot of time and productivity.
And ultimately, entire code bases can die because no one's able to fully understand the code.
So for example, here's the same example from before now slightly rewritten.
clean-code-1.py
To be precise, I basically only chose different names.
And now automatically, it becomes cleaner, it becomes easier to read and understand.
It won't take you as long to understand what's going on here as it did before.
And we could, of course, also refactor this in other ways.
We could, for example, also consider creating a class with good names and with all the validation logic baked into the class.
Something like this.
clean-code-1.py
And of course, just to make this clear right away, there will not be a single right way of writing clean code.
Instead, this is one possible solution.
Using a factory function with better names would have been another solution.
Ultimately, it's code which is readable and understandable:
code which is readable and meaningful
reduces the cognitive load you have to go through to understand what is written
should be concise and to the point
avoid unintuitive names, complex nesting or big code blocks
follow common best practices and patterns
should be fun to write and to maintain
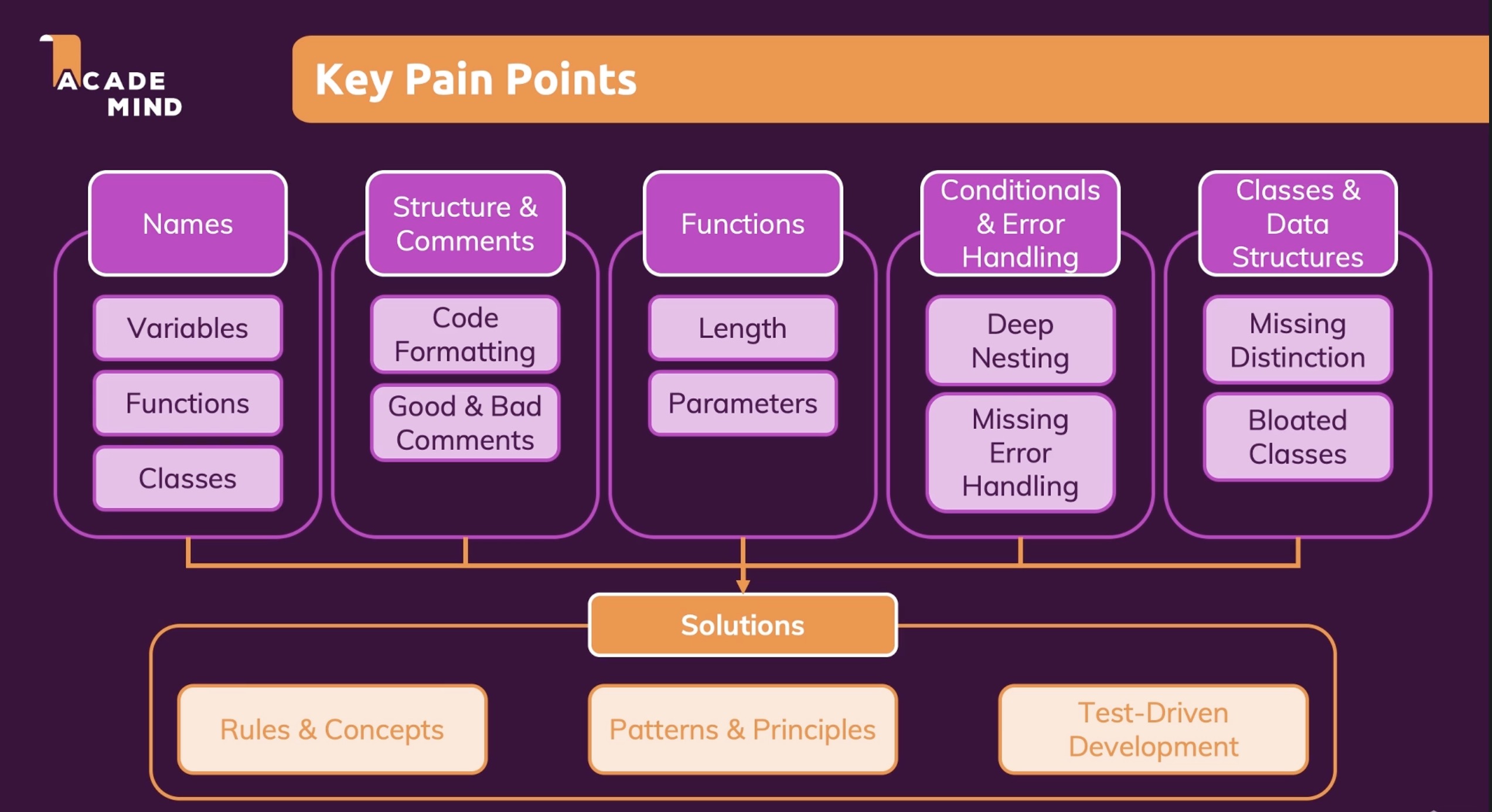
Key Pain Points
Naming
variables
functions
classes
Structure and comments
code formatting
good & bad comments
Functions
length
parameters
Conditionals & error handling
deep nesting
missing error handling
Classes & data structures
missing distinction
bloated classes
Section 2 - Naming - Assigning Names to Variables, Functions, Classes & More
Naming things can sometimes seem like an art form in programming because there are so many different ways
Why Good Names Matter
Names should be meaningful
bad-code.js
In this example, MainEntity doesn't tell me anything about its purpose nor does "us" mean a person who logs into our system.
It's not clear from just these two lines of code how they relate to each other without additional context.
On the flip side: good-code.js
Here we have more descriptive names that make it easier for someone else reading or maintaining your codebase later on
Well named "Things" allows the readers to understand your code without going through it in detail
We will not always agree
const admin = new Admin(); This is readable const admin = new AdminUser(); So is this
Choosing Good Names
How to Name Things Correctly
Variables & Constants | Functions/Methods | Classes |
|---|---|---|
Data containers | Commands or calculated values | Use classes to create "things" |
e.g. user input data, validation results, a list of products | e.g. nd data to a server, check if user input is valid | e.g. a user, a product, a http request |
Use nouns or short phrases with adjectives | Use verbs or short phrases with adjectives | Use nouns or short phrases with nouns |
|
|
|